If you want to easily test your functions in Haskell, you can do so by writing inputs and their expected responses right above your functions as comments. All you need is doctest.
This is how:
1. Setup Project
Let's setup a basic project first.
-
Install Haskell Stack if you don't have it already.
-
Setup project and install required dependencies.
stack new my-project
cd my-project
stack setup
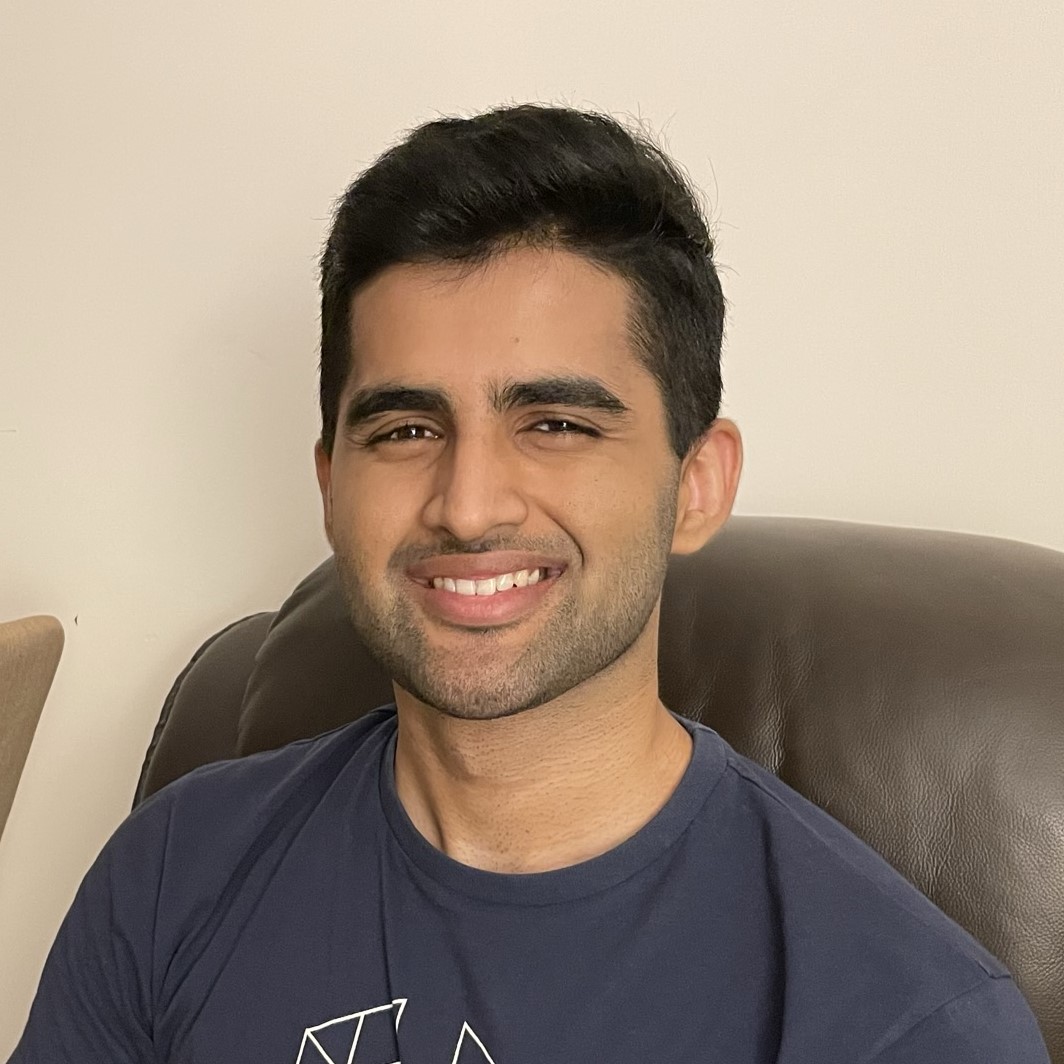
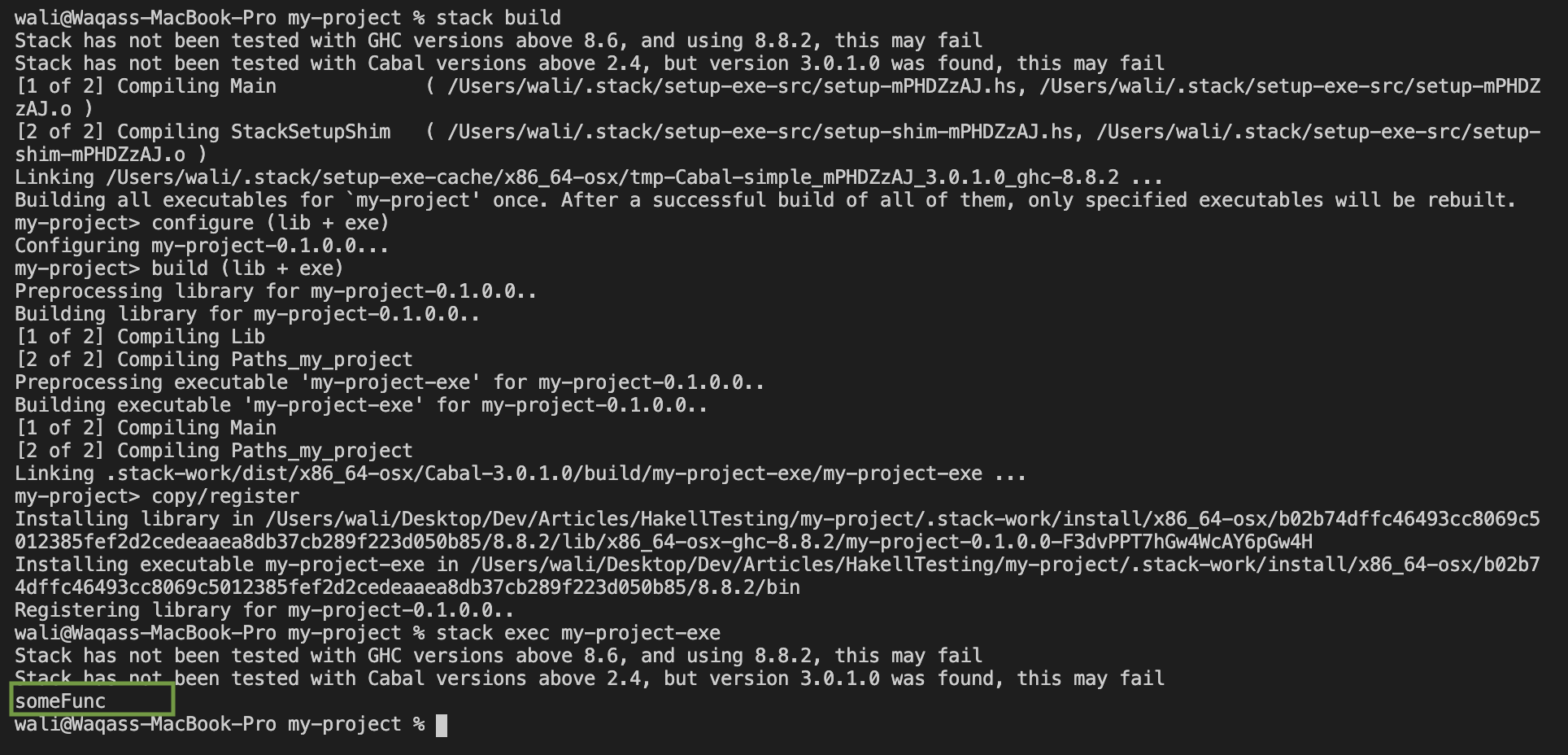
- Build and execute project. If you see
someFuncin the output you are good to go.
stack build
stack exec my-project-exe
2. Write a function
Let's write a simple function so we can test it.
- Create a file
Math.hsinsrcwith asquarefunction:
module Math where
square :: Int -> Int
square x = x * x
-
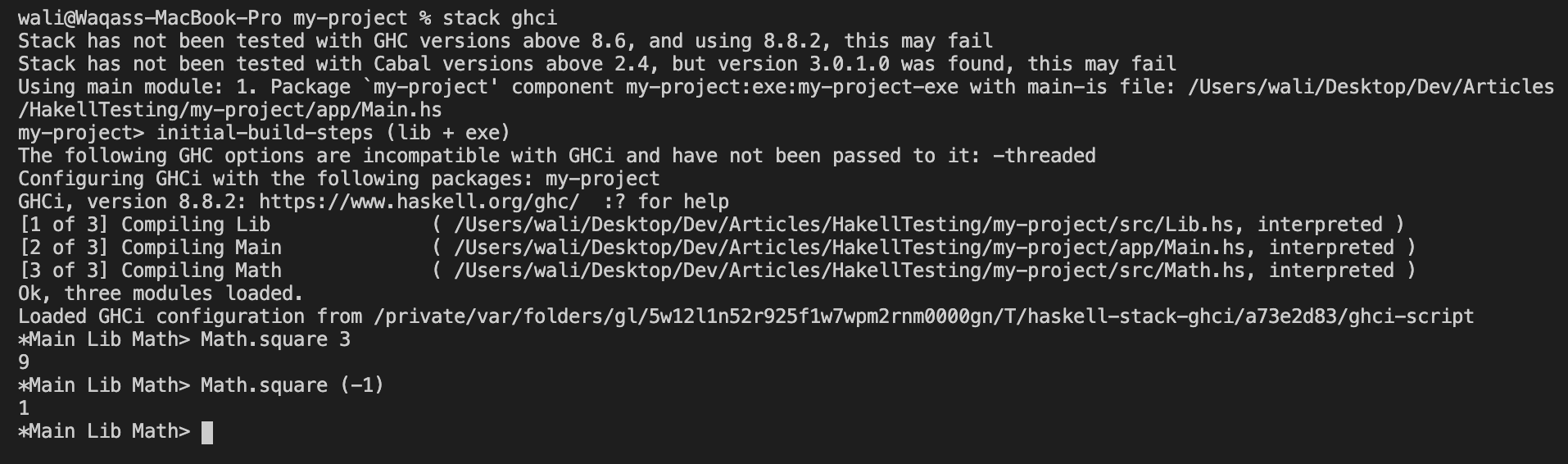
Manually test the function in GHCi. Load up the interactive environment using
stack ghci. -
Try out the function to see everything is working as expected:
Math.square 3should output9.
3. Write tests
Now let's get to the actual testing. All we need to do to is write comments.
- Just above your function definition, write your set of inputs and their expected outputs. This is how my
Math.hslooks like:
module Math where
-- | Square numbers
--
-- Examples:
--
-- >>> square 3
-- 9
--
-- >>> square (-1)
-- 1
square :: Int -> Int
square x = x * x
- If you try running
stack testyou will notice these tests don't run. That's because we haven't set updoctestyet.
4. Configure Project for doctest
- First, let's add
doctestto our project. Go to the end ofpackage.yamland add it as dependency ofmy-project-test. This is how mypackage.yamllooks like:
name: my-project
version: 0.1.0.0
github: "githubuser/my-project"
license: BSD3
author: "Author name here"
maintainer: "example@example.com"
copyright: "2020 Author name here"
extra-source-files:
- README.md
- ChangeLog.md
# Metadata used when publishing your package
# synopsis: Short description of your package
# category: Web
# To avoid duplicated efforts in documentation and dealing with the
# complications of embedding Haddock markup inside cabal files, it is
# common to point users to the README.md file.
description: Please see the README on GitHub at <https://github.com/githubuser/my-project#readme>
dependencies:
- base >= 4.7 && < 5
library:
source-dirs: src
executables:
my-project-exe:
main: Main.hs
source-dirs: app
ghc-options:
- -threaded
- -rtsopts
- -with-rtsopts=-N
dependencies:
- my-project
tests:
my-project-test:
main: Spec.hs
source-dirs: test
ghc-options:
- -threaded
- -rtsopts
- -with-rtsopts=-N
dependencies:
- my-project
- doctest
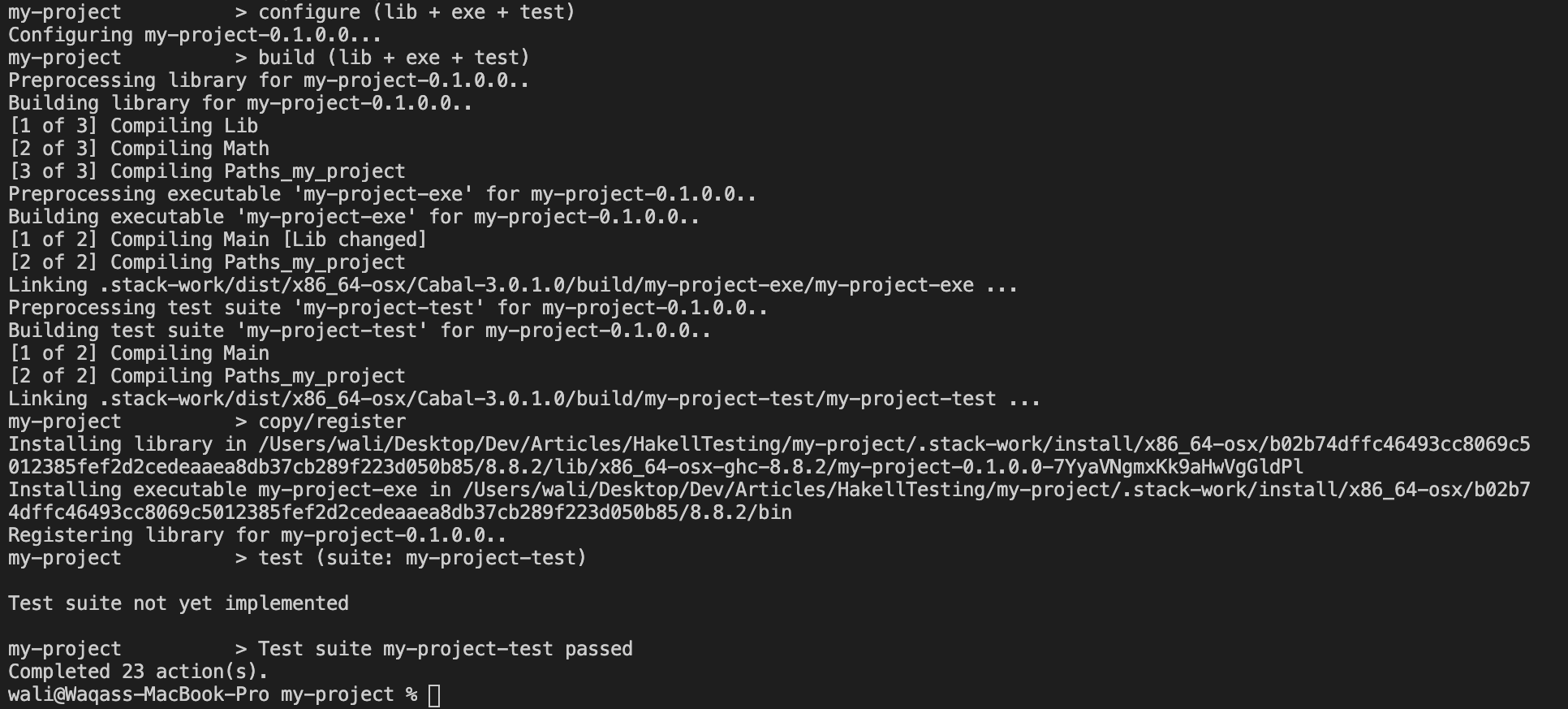
- To install the dependency, run
stack test. If the installation goes well, you should see the following messageTest suite not yet implemented.
If you go to the actual test file in test/Spec.hs you can see that there indeed are no tests. We need to somehow tell stack to look for tests in our src files instead.
- To do that, clear the contents of
test/Spec.hsfile and replace it with this:
import Test.DocTest
main = doctest ["-isrc", "src/Math.hs"]
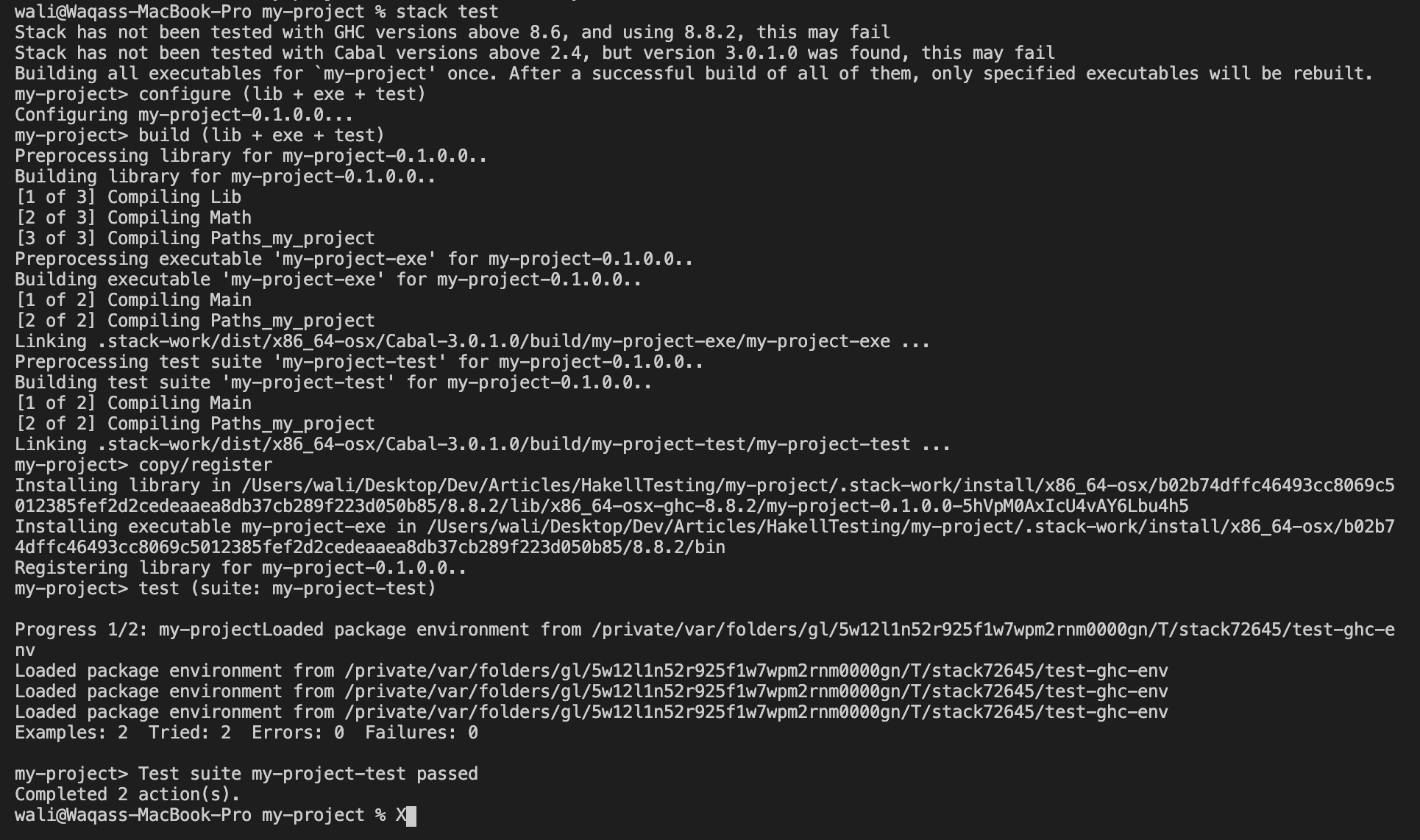
- Now, if you run
stack testit will run the 2 tests we wrote earlier. That's it, we are done!
When you add more modules, simply add them to this list ["-isrc", "src/Math.hs"] in test/Spec.hs to make doctest look for tests in them.
Note
This was my setup while writing this:
- MacOS
10.15.3 - Haskell Stack
2.1.3
